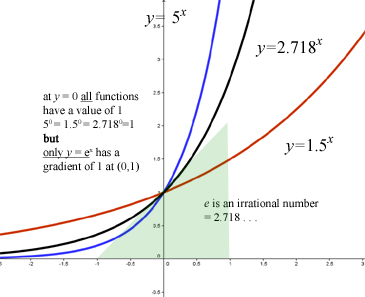
This problem has been solved!In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable, denoted or , is a generalization of the weighted average, and is intuitively the arithmetic mean of a large number of independent realizations of The expected value is also known as the expectation, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first momentExpected value is a key concept in economics, finance, and manyY=e^x Loading y=e^x y=e^x Log InorSign Up y = e x 1 y = k

A Sketch The Graph Of Y Ex As A Curve In R2 B Sketch The Graph Of Y Ex As A Surface In R3 C Describe And Sketch The Surface Z Ey Study Com
Y do vertice
Y do vertice-E (Y) = Sum (y P (Y = y)) where P (Y = y) is the probability that the random variable Y takes on the value y, and the sum extends over all possible y In a similar fashion E (X Y) = Sum (z P (X Y = z)) where the sum extends over all possible values of z Thus you are looking at all possible combinations of values of X and Y that add to z Visit http//ilectureonlinecom for more math and science lectures!In this video I will find the solution to y'y=e^x, with initial value y(0)=1 (a linear no




The Logarithm And Exponential Functions
In this video I go over how to graph the natural exponential function or y = e^x in a step by step fashion This is one of the most important functions in al==> y' = y*(e^x)*lnx /x Approved by eNotes Editorial Team We'll help your grades soar Start your 48hour free trial and unlock all the summaries, Q&A, and analyses you need to get betterThis might feel a bit more difficult to graph, because just about all of my yvalues will be decimal approximationsBut if I round off to a reasonable number of decimal places (one or two is generally fine for the purposes of graphing), then this graph will be fairly easy
Definition 2 The exp function E(x) = ex is the inverse of the log function L(x) = lnx L E(x) = lnex = x, ∀x Properties • lnx is the inverse of ex ∀x > 0, E L = elnx = x • ∀x > 0, y = lnx ⇔ ey = x • graph(ex) is the reflection of graph(lnx) by line y = x • range(E) = domain(L) = (0,∞), domain(E) = range(L) = (−∞,∞)Graph y = e x; If y = e^x (sin x cos x), then show that d^2y/dx^2 2dy/dx 2y = 0 asked in Mathematics by Samantha ( 3k points) continuity and differntiability
Break at uniformly chosen point Y • Conditional expectation break again at uniformly chosen point XLECTURE 12 Conditional expectations • Readings Section 43;Mathx^y=e^{xy}/math math\ln(x^y)=xy/math mathy\ln(x)=xy/math mathy(\ln(x)1)=x/math mathy=\dfrac{x}{\ln(x)1}/math math\dfrac{\mathrm dy



The Derivative Of Exponentials Logarithms Differential Calculus Pure Mathematics From A Level Maths Tutor



Euler S Number E
Graph y=e^x3 y = ex − 3 y = e x 3 Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote The equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = −3 y = 3 Horizontal Asymptote y = −3 y = 3 3 Find the general solution for y" y'=e^ x –sin(x) Solution First find the homogeneous solution yh'' yh' = 0 The characteristic equation is m2 m = 0 m(m 1) = 0 m = 0 or m = 1 Thus yh(x) = A Bex Now for the particular{eq}\int_1^4 \int_0^{\sqrt{y}} e^{x/\sqrt{y}}dxdy {/eq} Integrals Some integrals look pretty bad from the start, but turn out to be pretty straightforward This is exactly the case here, where




Exponential Function Wikipedia



Search Q Ln X Tbm Isch
E−λ = λ The easiest way to get the variance is to first calculate EX(X −1), because this will let us use 0 You can use the definition of an expectation E (XY) = x*y*f (x,y) dy dx Or you could argue that since the function is symmetric about 0 and the intervals 1, 1 are centred about 0 that E (XY) = 01 You are quite close to the answer Since you've already deduced that the critical points are where the following equations hold e x s i n ( y) = 0 e x c o s ( y) = 0 Thus all that's left to do is to solve it Consider what happens when we set f x to 0 f x = e x s i n ( y) = 0 Thus, f x takes on the value of zero when either e x = 0 (not




1 9 Limit Of Exponential Functions And Logarithmic Functions Mathematics Libretexts
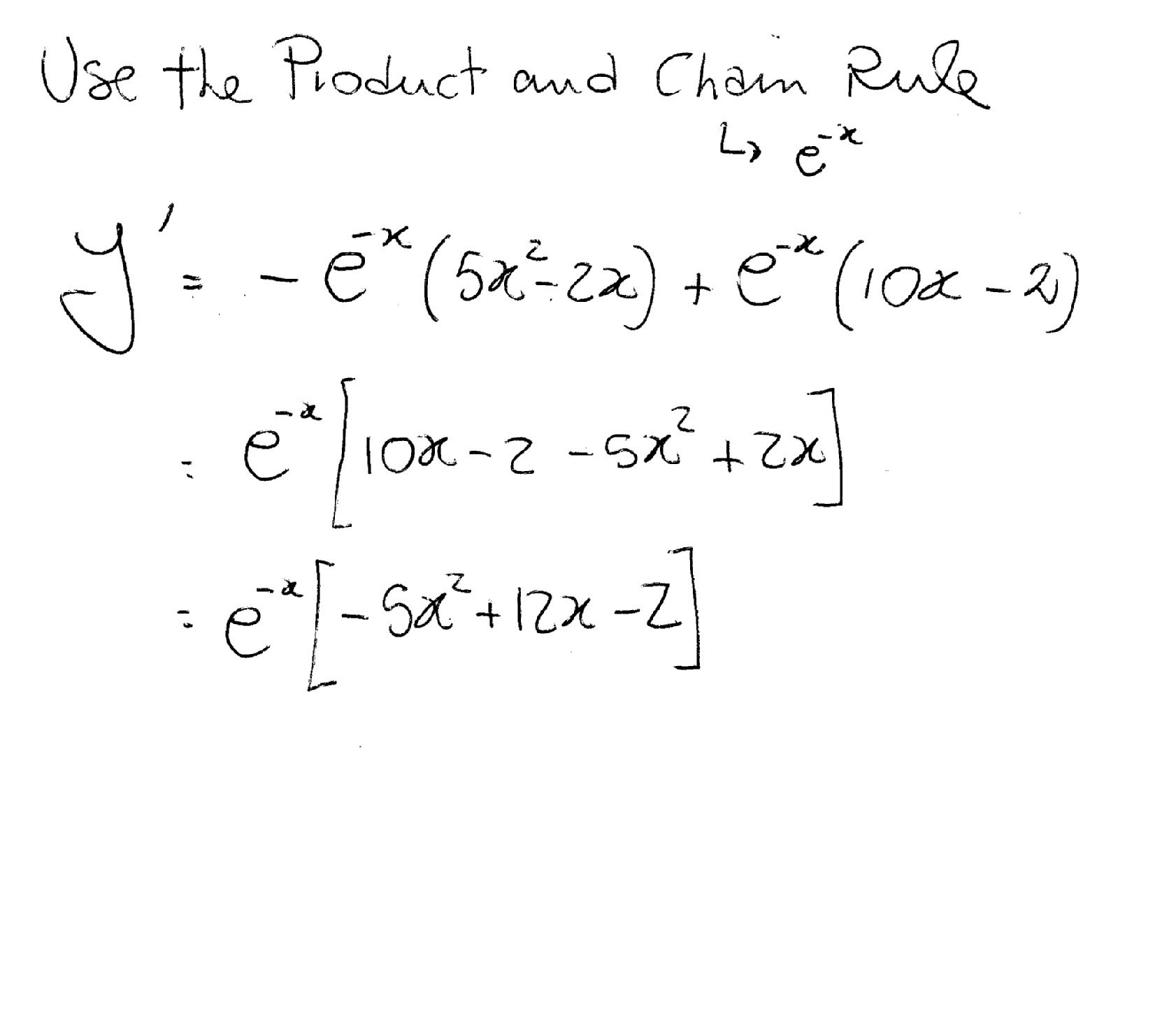



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y E X 5x 2 2x Socratic
E−λ = λ X∞ k=0 λk k!= λ X∞ k=1 λ λk−1 (k −1)!Answer to Solve the differential equation x dy/dx y =e^x, x>0 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework



Natural Exponential Function And Natural Logarithmic Function Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math
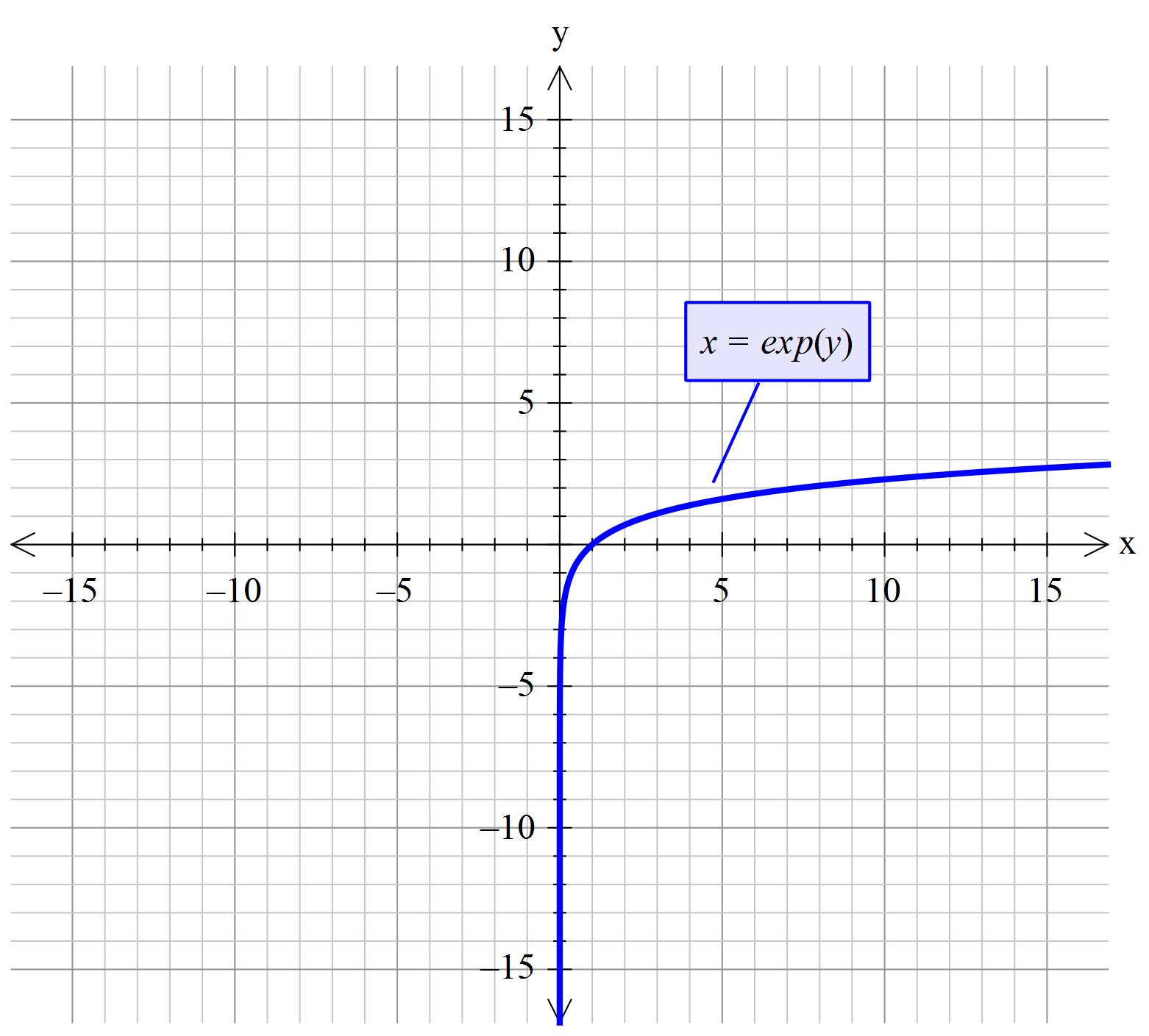



How Do You Graph X E Y Socratic
The expression for the derivative is the same as the one for the original function That is The derivative of e x is e x The derivative of e x is e x This is one of the properties that makes the exponential function really important Now you can forget for a while the series expression for the exponential We only needed it here to prove theSee the answer y=e^x, y=1, x=2 about y=2 so I have A= pi (2e^x)^2pi (1) and then V= pi* the integral from 0 to 2 of e^2x 4e^x3 dxXY (x y) (mean and variance only;



The Solution Of Dy Dx Y E X Y 0 0 Is Studyrankersonline




General Solution Of Differential Equation Y 3y E X Mathematics Stack Exchange
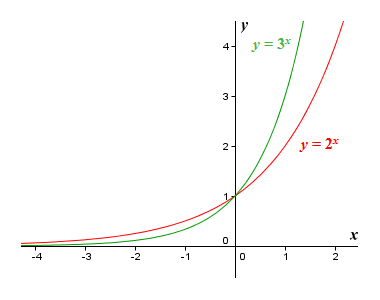
More generally, an exponential function is a function of the form f ( x ) = a b x , {\displaystyle f (x)=ab^ {x},} where b is a positive real number, and the argument x occurs as an exponent For real numbers c and d, a function of the form f ( x ) = a b c x d {\displaystyle f (x)=ab^ {cxd}} is also an exponential function, since it can be Let X and Y be discrete random variables Prove the linearity of expectation E(XY) = E(X) E(Y) An exercise problem in probability theory The solution is givenTransforms) x (integral in continuous case) Lecture outline • Stick example stick of length!
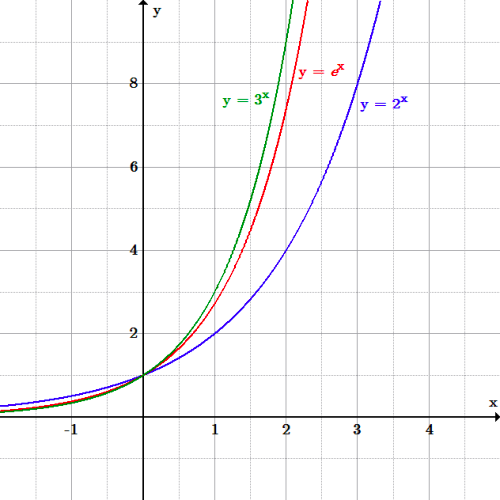



The Real Number E Boundless Algebra
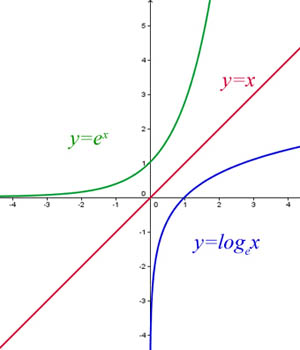



The Derivative Of Exponentials Logarithms Differential Calculus Pure Mathematics From A Level Maths Tutor
46 Expectation of XY the definition of E(XY) Suppose we have two random variables, X and Y These might be independent, in which case the value of X You state up front that y= ex y = e x More generally, y = f (x) After stating this, you cannot later just play like 'y' is NOT a function of 'x' It is NOT a constant, here You are overlooking a constant of integration Even if you were right about 'y' being constant, you should be left with y = xy C ==> 1 = x C/yCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and




If Y Ex Tan 1 X Prove That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 2 1 X X2 Dy Dx 1 X 2 Y 0 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




Transforation Of Exponential Graphs Y Ex Matching Cards With Answers Teaching Resources
यदि x और y यादृच्छिक चर इस प्रकार हैं जिससे e2x y = 0 और ex 2y = 33 हैं, तो ex ey का मान क्या है? If y = ex e– x, prove that dy/dx = √(y2 – 4) Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to getThe basic answer is yes, this is simply the multiplicative rule for indices For a number matha/math, the general rule is matha^x \cdot a^y = a^{xy}/math Intuitively for nonnegative integers we can identify these symbols as "matha/ma




Resuelva Por Coeficientes Indeterminados Y Variacion De Parametros By Gerson Villa Gonzalez Issuu




If Y Ex Sinx Cosx Prove That D2y Dx2 2dy Dx 2y 0 Please Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com
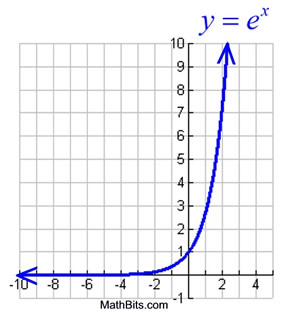
If Y = E X E − X Prove that D Y D X = √ Y 2 − 4 ?Ask Question Asked 6 years, 4 months ago Active 6 years, 4 months ago Viewed 38k times 3 2 $\begingroup$ I am studying probability and trying to follow an example in my textbook discussing expectation of the sum of random variables But I'm having trouble following itSlope itself, y = exp(x) or y = e x The exponential function is a power function having a base of e This function takes the number x and uses it as the exponent of e For values of 0, 1, and 2, the values of the function are 1, e or about 2718, and e² or about



Area Of A Surface Of Revolution



Ocw Mit Edu Resources Res 6 012 Introduction To Probability Spring 18 Part I The Fundamentals Mitres 6 012s18 L13as Pdf
Answer to Calculate d2y dx2 y = e−x ex Find solutions for your homework or get textbooks SearchEcon 1A Ramu Ramanathan Spring 03 Answers to Exam #2 I Let X and Y be two random variables, with means µ x and µ y, Var(X) = 2 = E(X σX 2) − 2, Var(Y) = = E(Y µX 2 σY 2) − 2, and Cov (X, Y) = µY σXYNow make the transformations U = X Y, and V = X − Y (a) (3 points) Derive E(U) and E(V) in terms of µX and µYLet's take the derivative of what well let's prove what the derivative of e to the X is and and I think that this is one of the most amazing things depending on how you view it about either calculus or math or the universe so we want to figure out but we're essentially going to prove we've I've already told you before that the derivative of e to the X is equal to e to the X which is amazing
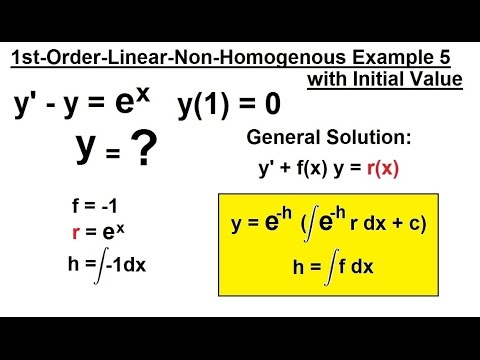



Differential Equation 1st Order Linear Form 8 Of 9 Example 5 Of Non Homogenous Form Youtube




Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx
3 Eliminate the exponent Using the rules of logarithms, this equation can be simplified to eliminate the exponent The exponent within the logarithm function can be removed as a multiple in front of the logarithm, as follows ln y = x ln a {\displaystyle \ln y=x\ln a} 4 Differentiate both sides and simplify• Given the value y of a rv Y parts of Section 45 EX Y = y= xpno!Suppose you know e −yx is invertible with inverse w You want to show that (e−xy) has an inverse that equals e xwy You can check this directly For example, (e− xy)(e xwy) = e−xyxwy− xyxwy = e −x(e−w yxw)y = e−x(e− (e− yx)w)y = e Divide by a number without dividing Divide by a number without dividing https//math
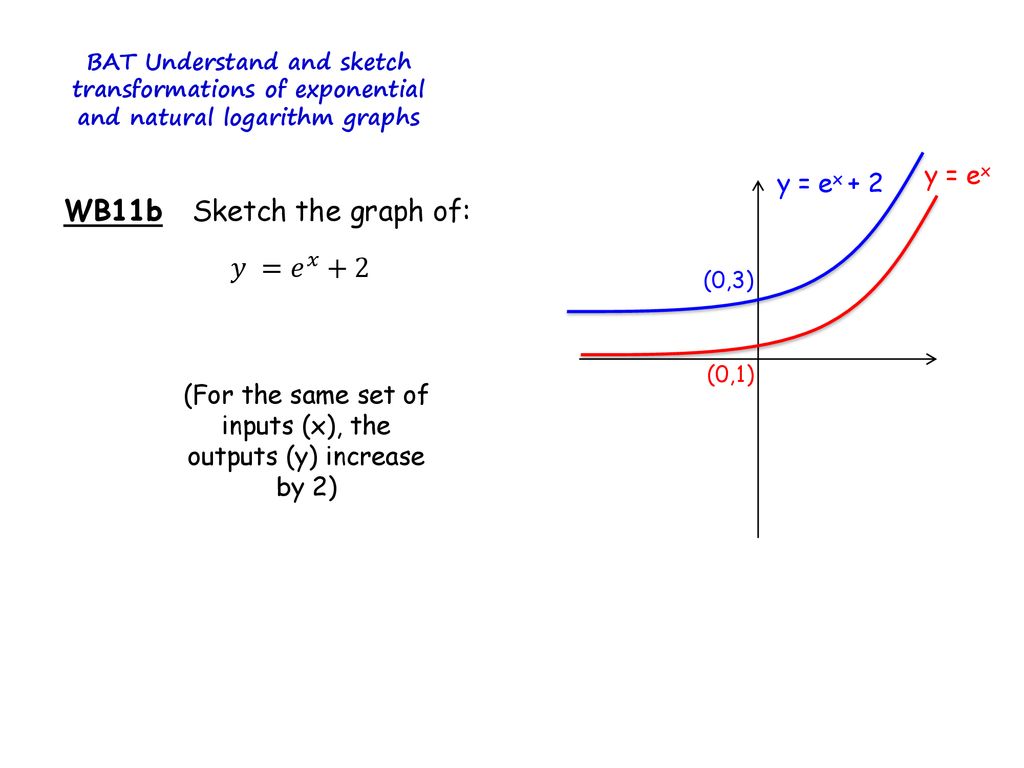



Exponential And Logarithms Transformations Graphs Ppt Download




E Xy E X E Y And Pull Out Property Of Conditional Expectation Without Standard Machine Mathematics Stack Exchange
Limit Definition Proof of e x Limit Definition By laws of exponents, we can split the addition of exponents into multiplication of the same base Factor out an e x We can put the e x in front of the limit We see that as h approaches 0, the limit will get closer to 0/0 which is an indeterminant form (meaning we don't really know what isClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If x^y = e^x y , then dydx is equal to Join / Login > 12th > Maths > Continuity and Differentiability > Derivatives of Implicit FunctionsCBSE CBSE (Science) Class 12 Question Papers 1851 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 4562 Question Bank Solutions 179 Concept Notes & Videos 725 Time Tables 18 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads



How To Sketch The Graph F X E X 1 Socratic



Logarithms
If X and Y are random variables such that E2X Y = 0 and EX 2Y = 33, then EX EY = _____One way to analyze the possible values the given function can take on is to transform it into the "simplest possible" form Some arithmetic we might apply could look like this y = e x e − x e x − e − x = e 2 x 1 e 2 x − 1 = 1 − e 2 x 1 2Sity function and the distribution function of X, respectively Note that F x (x) =P(X ≤x) and fx(x) =F(x) When X =ψ(Y), we want to obtain the probability density function of YLet f y(y) and F y(y) be the probability density function and the distribution function of Y, respectively Inthecaseofψ(X) >0,thedistributionfunctionofY, Fy(y), is rewritten as follows



Http Www Math Umass Edu Lr7q Ps Files Teaching Math456 Lecture16 Pdf




Find The Inverse Of F Where F X Frac E X E X E X E X Mathematics Stack Exchange
Using the formulas of integration ∫ e x d x = e x , we get e y = e x c ⇒ y = ln ( e x c) This is the required solution of the given differential equation ⇐ Solve the Differential Equation dy/dx=xy^2 ⇒ Solve Differential Equation dy/dx=xe^y ⇒EY = E (X EX)2 = var(X) We have then P(jX EXj ) = P((X EX)2 2) = P(Y 2) EY 2 = var(X) 2 (1) Independence and sum of random variables Two random variables are independent independent if the knowledge of Y does not in uence the results of Xand vice versa This 3Var(XjY =y)=E(X2jY =y)¡E(XjY =y)2 Remark We always suppose that åx jg(x)jfXjY(xjy)•¥ Definition Denote j(y) = E(XjY = y) Then E(XjY) def= j(Y) In words, E(XjY) is a random variable which is a function of Y taking value E(XjY =y) when Y =y The E(g(X)jY) is defined similarly In particular E(X2jY) is obtained when g(X)=X2 and Var




Ex 9 3 5 Form Differential Equation Y Ex A Cos X B Sin X
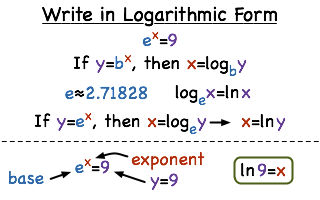



How Do You Convert From Exponential Form To Natural Logarithmic Form Printable Summary Virtual Nerd
How to understand the proof of EXY = EX EY?Graph y=e^ (x) y = e−x y = e x Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote The equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 y = 0 Horizontal Asymptote y = 0 y = 0 Explanation Given y = e−x Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that, dy dx = dy du ⋅ du dx Let u = − x, ∴ du dx = −1 Then, y = eu, dy du = eu Combine the results together to get dy dx = eu ⋅ −1 = − eu



1
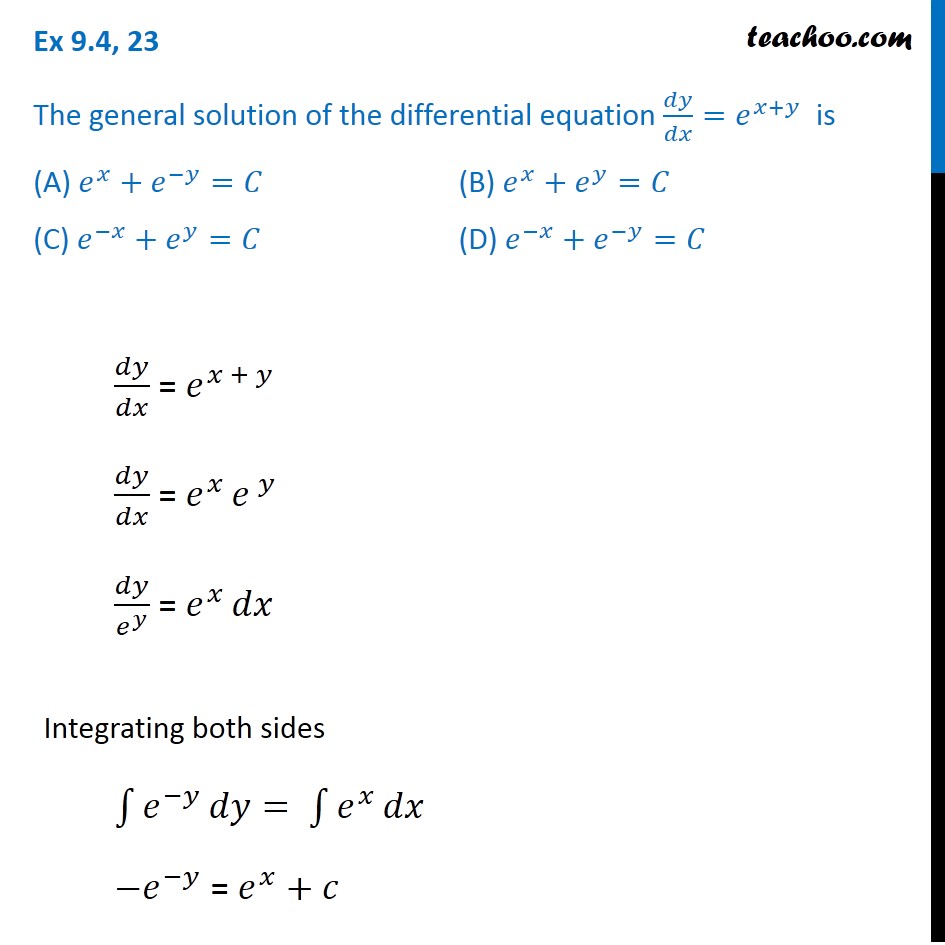



Ex 9 4 23 General Solution Of Dy Dx E X Y Is A E X E Y C




How To Draw Graph Of F X E X2 Quora
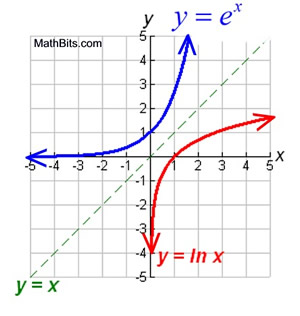



Natural Exponential Function And Natural Logarithmic Function Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math




15 6 Calculating Centers Of Mass And Moments Of Inertia Mathematics Libretexts



Q Tbn And9gcsqdohwlqv7hezevkttjajjqlrfahan470gq5zvj62tldxf6ujk Usqp Cau
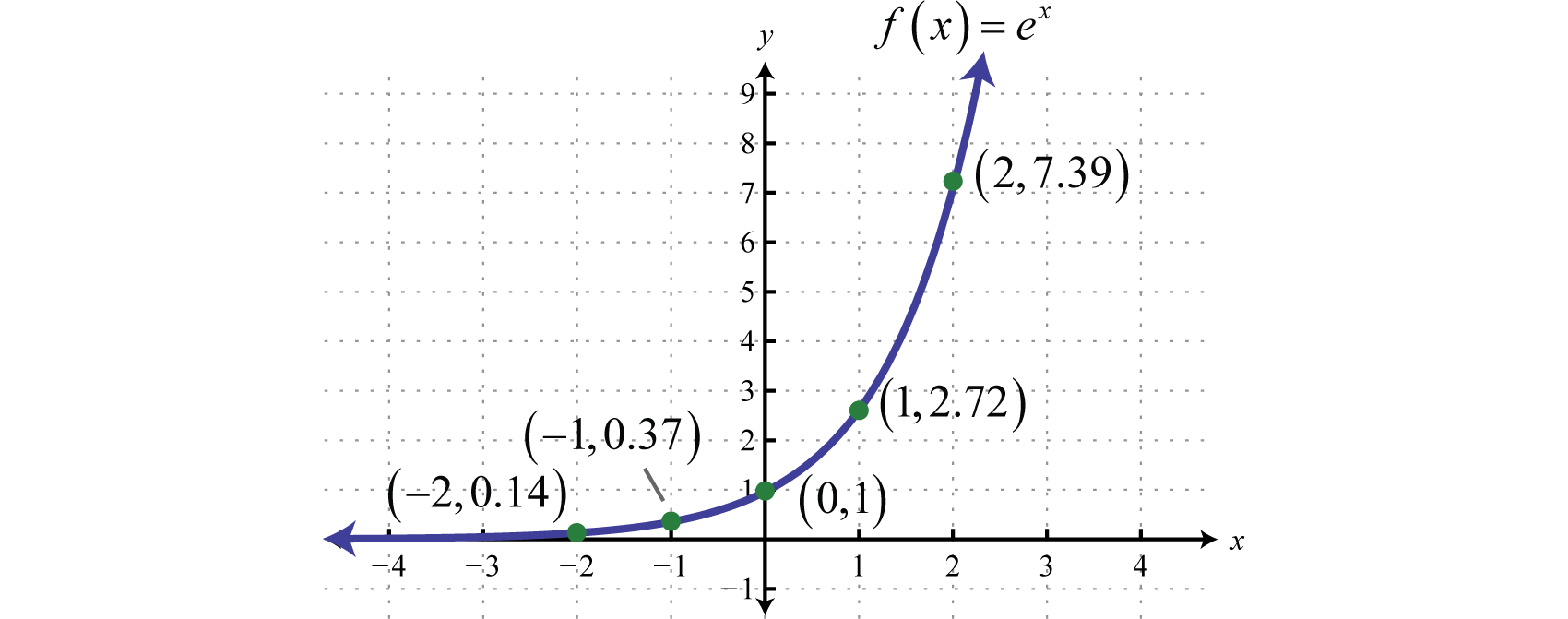



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs




Exponential Function Wikipedia




The Logarithm And Exponential Functions



Search Q 1 X Graph Tbm Isch



Definition Of Covariance The Covariance Of X Y
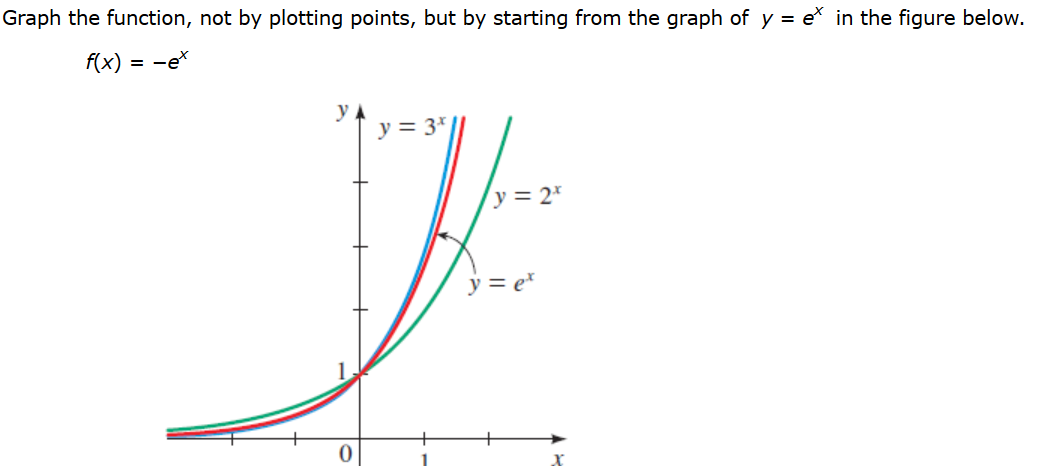



Graph The Function Not By Plotting Points But By Chegg Com




A Sketch The Graph Of Y Ex As A Curve In R2 B Sketch The Graph Of Y Ex As A Surface In R3 C Describe And Sketch The Surface Z Ey Study Com




Probability Covariance And Correlation Faisalkhan81 Yahoo Com



Www Math Uh Edu Jiwenhe Math1432 Lectures Lecture04 Handout Pdf




Working With Exponentials And Logarithms
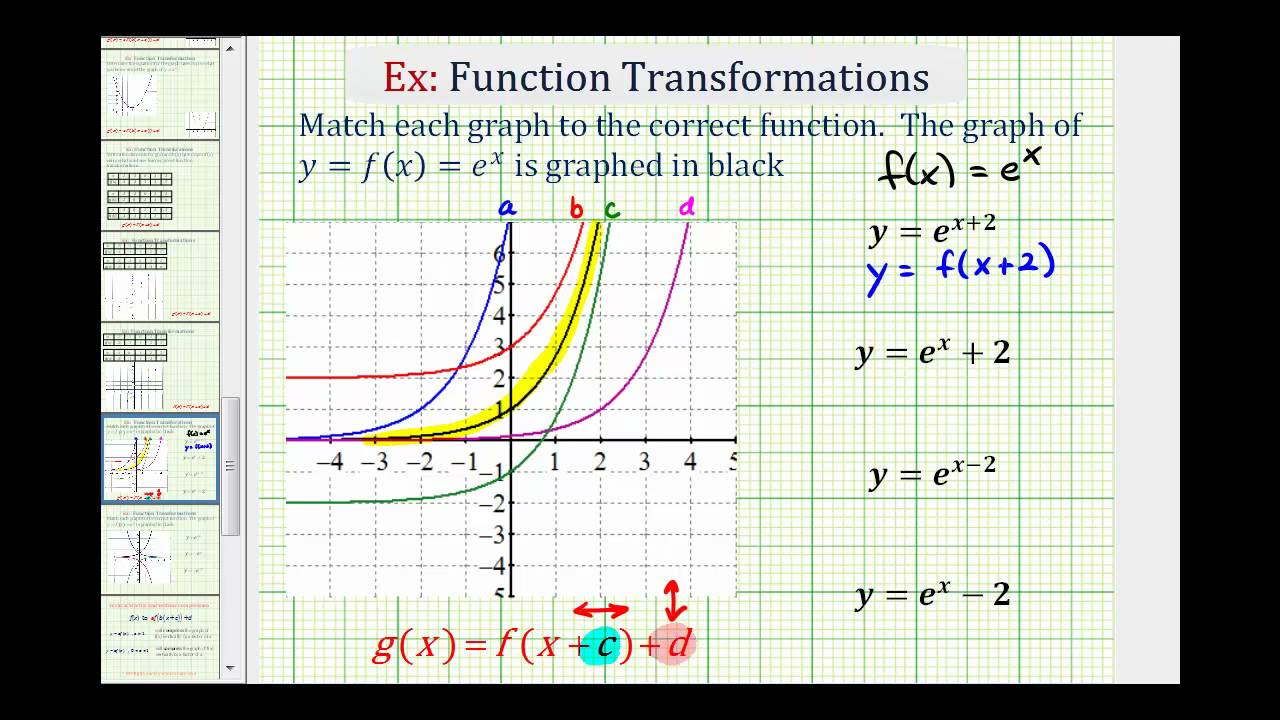



Horizontal And Vertical Translations Of Exponential Functions College Algebra




If Y E X Cot X Then Dy Dx Will Be



Solution Use The Graph Of Y E X To Evaluate E 1 6 To Four Decimal Places




Introduction We Are Going To Look At Exponential Functions We Will Learn About A New Special Number In Mathematics We Will See How This Number Can Be Ppt Download




If Y E X Cos X And Y N K Ny 0 Where Yn D Ny Dx N And



How To Find X And Y Intercepts Of Graphs



If Y E X A Cos X B Sin X Then Y Is A Solution Of Studyrankersonline




Solve X Dy Dx Y X 1 Ex Brainly In




The Solution Of The Differential Equation Dy Dx 1 E X Y I
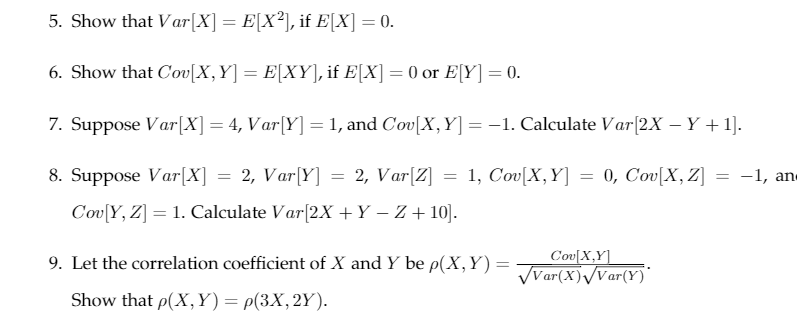



Show That Var X E X 2 If E X 0 Show That Chegg Com
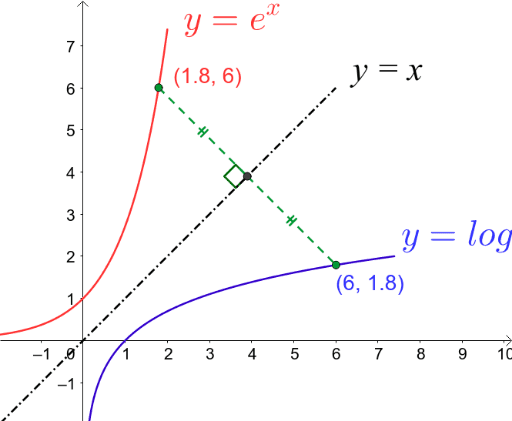



Graphs E X And Ln X Geogebra




Working With Exponentials And Logarithms




Proof The Derivative Of 𝑒ˣ Is 𝑒ˣ Video Khan Academy



What Is The Graph Of E X Quora
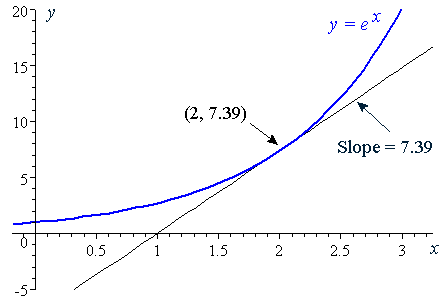



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function




E Mathematical Constant Wikipedia




Solve D 3y Dx 3 3 D 2y Dx 2 3 Dy Dx Y E X 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection



Bestmaths
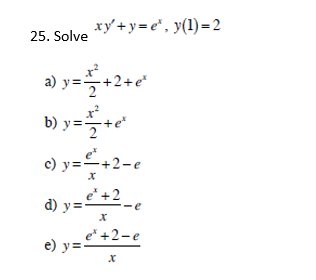



Solve Xy Y E X Y 1 2 A Y X 2 2 2 E X Chegg Com




If Y E X E X E X E X Prove That Dy Dx 1 Y 2



Arc Length



If Ex Ey Ex Y Then Dy Dx Quora



Ocw Mit Edu Resources Res 6 012 Introduction To Probability Spring 18 Part I The Fundamentals Mitres 6 012s18 L07 Pdf



Content Graphing Logarithmic Functions



If X Y E X Y Show That Dy Dx Logx Log Xe 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Review



Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch3annotated Pdf
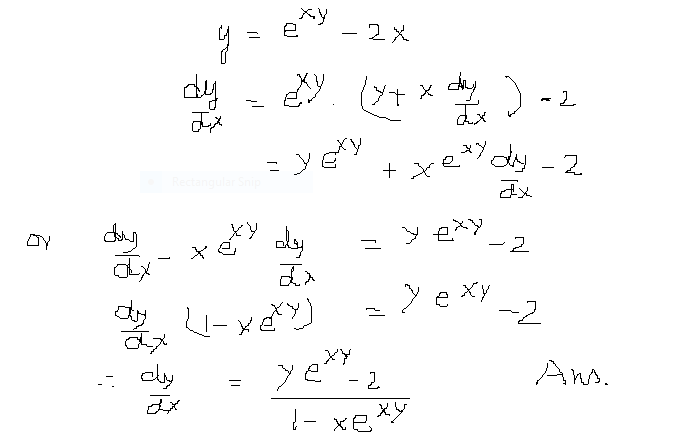



How Do You Differentiate Y E Xy 2x Socratic



Derivative Of E X Wyzant Lessons
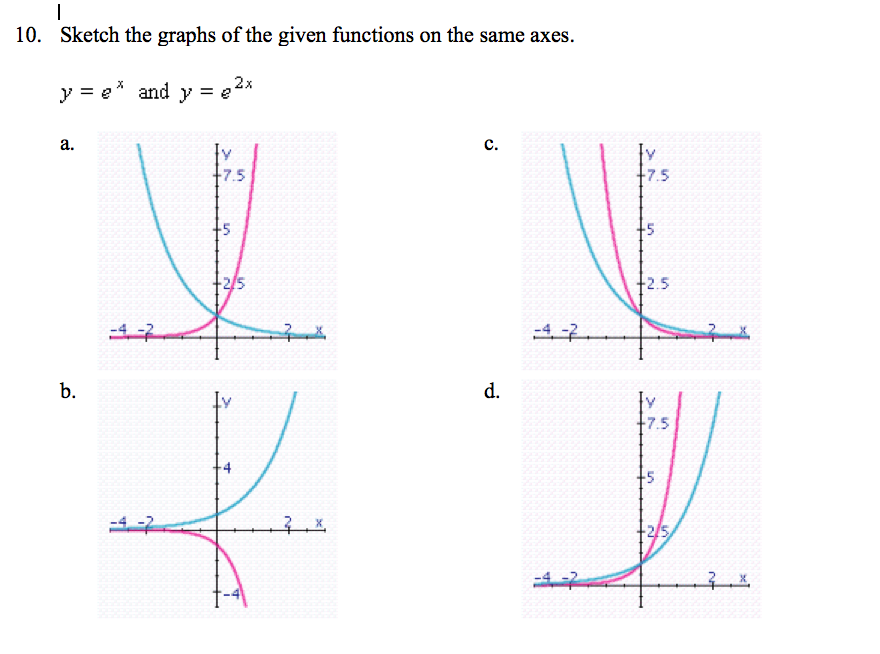



Sketch The Graphs Of The Given Functions On The Same Chegg Com



Find The General Solution Of Y Y 2y Ex 1 Ex Stumbling Robot



Euler S Number E




If Y E X Sin X Cos X Then Show That D 2ydx 2 2 Dydx 2y 0



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs



Solve The Equation D 2 2d 1 Y E X 3 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Differential Equation Variation Of Parameters Y 2y Y E X Ln X Youtube



Graphing The Natural Exponential Function Y E X Youtube
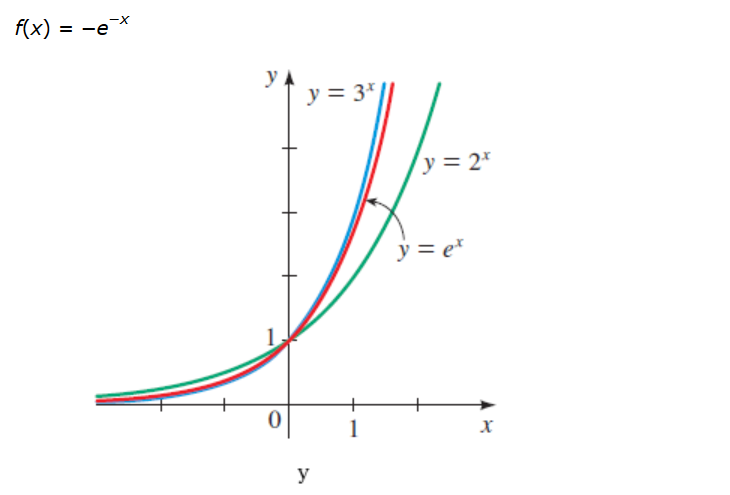



Graph The Function Not By Plotting Points But By Chegg Com




Flat Function Wikipedia



Solution Y E X How Do I Graph This Please Help




Natural Logarithms




Misc 18 General Solution Ex Dy Y Ex 2x Dx 0 Miscellaneous



Function And Relation Library




Find F X That Minimizes E Y F X 2 X Mathematics Stack Exchange
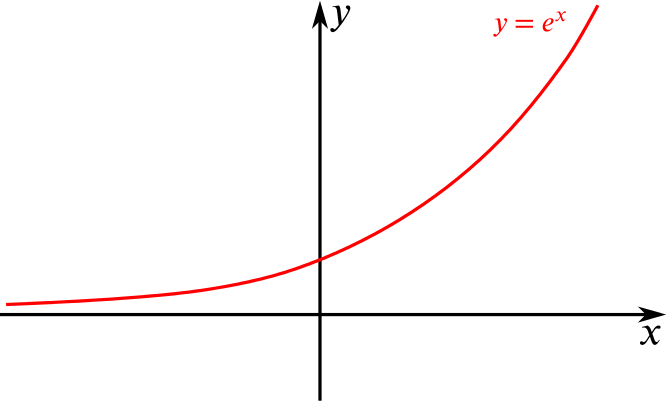



Solution Can We Sketch And Describe These Composite Functions Combining Functions Underground Mathematics




12 3 Exponential Functions




If Y Ex Sin X Prove That D2y Dx2 2 Dy Dx 2y 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com 5p09j033




Ex 9 5 10 Show Homogeneous 1 Ex Y Dx E X Y 1 X Y
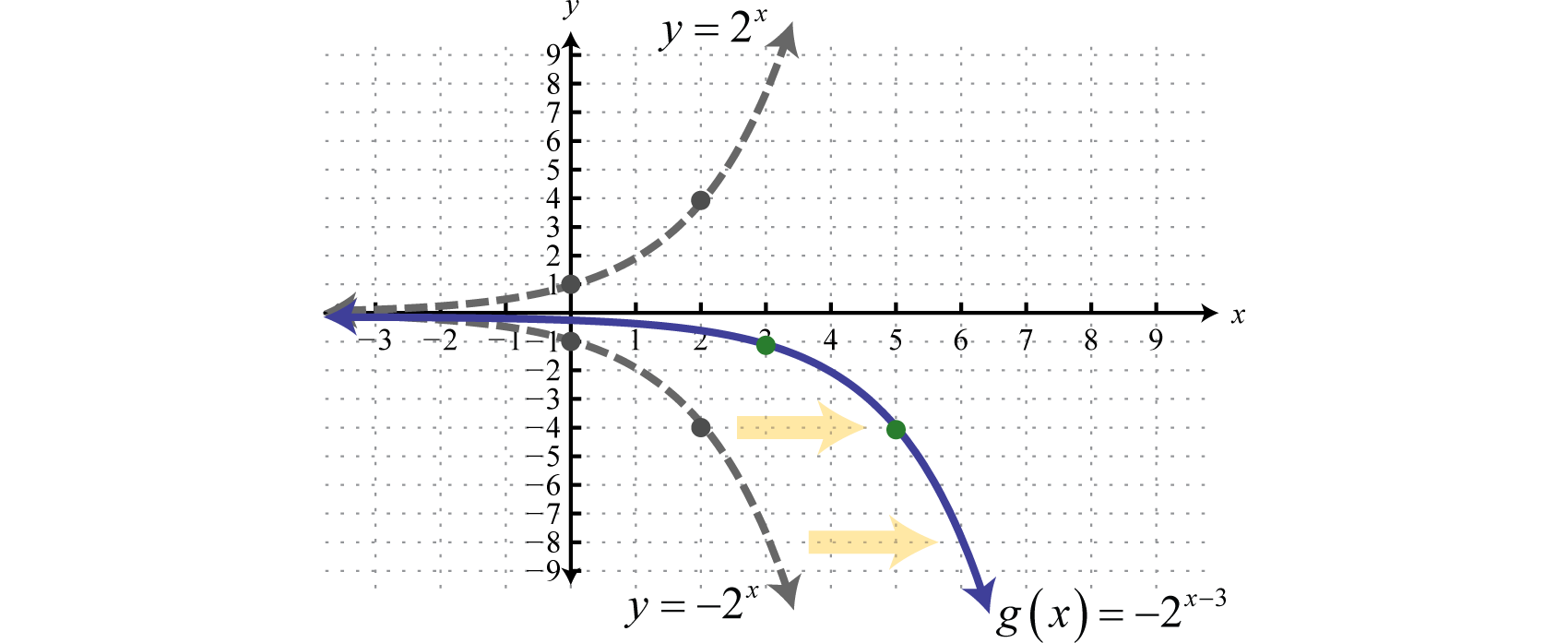



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs




Review
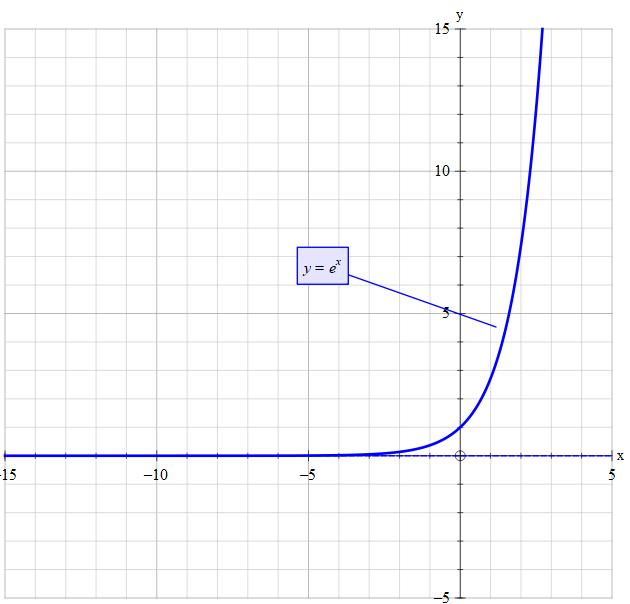



What Is The Domain And Range Of Y E X Socratic




If Y E Tanx Then Dy Dx Is Equal To Brainly In
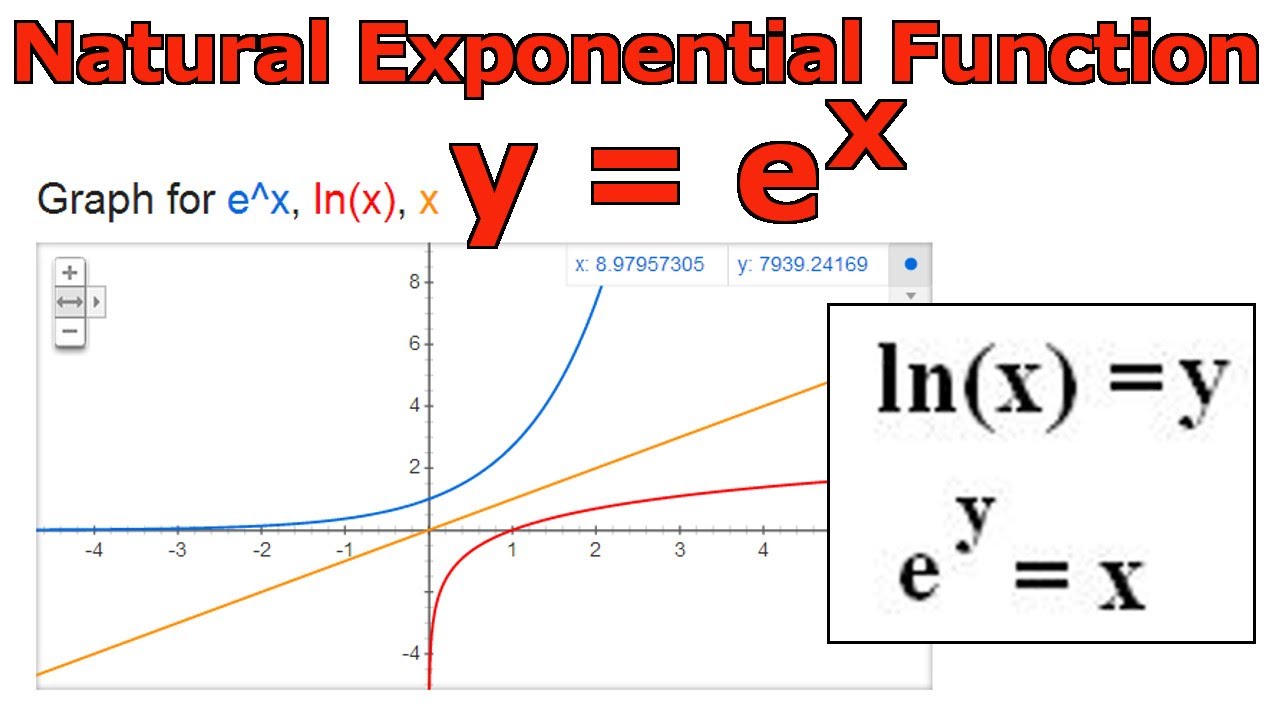



Natural Exponential Function Y E X Youtube




Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 E X Y Dx E X Y 1 X
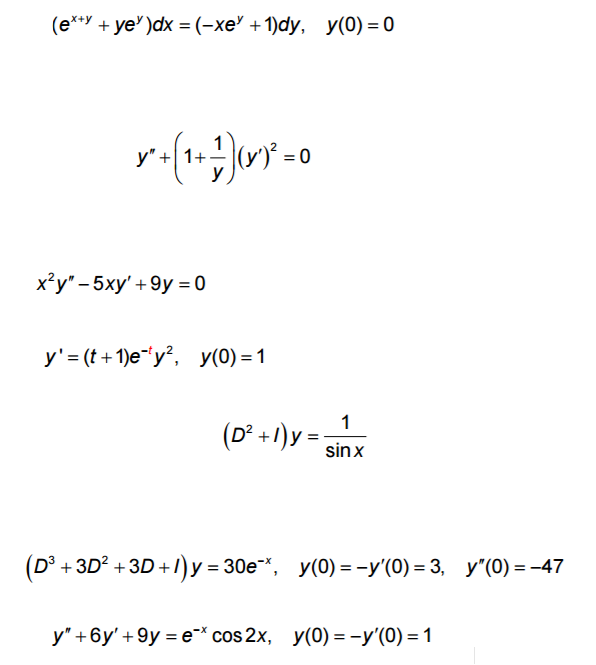



E X Y Ye Y Dx Xe Y 1 Dy Y 0 0 Y 1 Chegg Com




X E Y Zonealarm Results



Exponential Functions
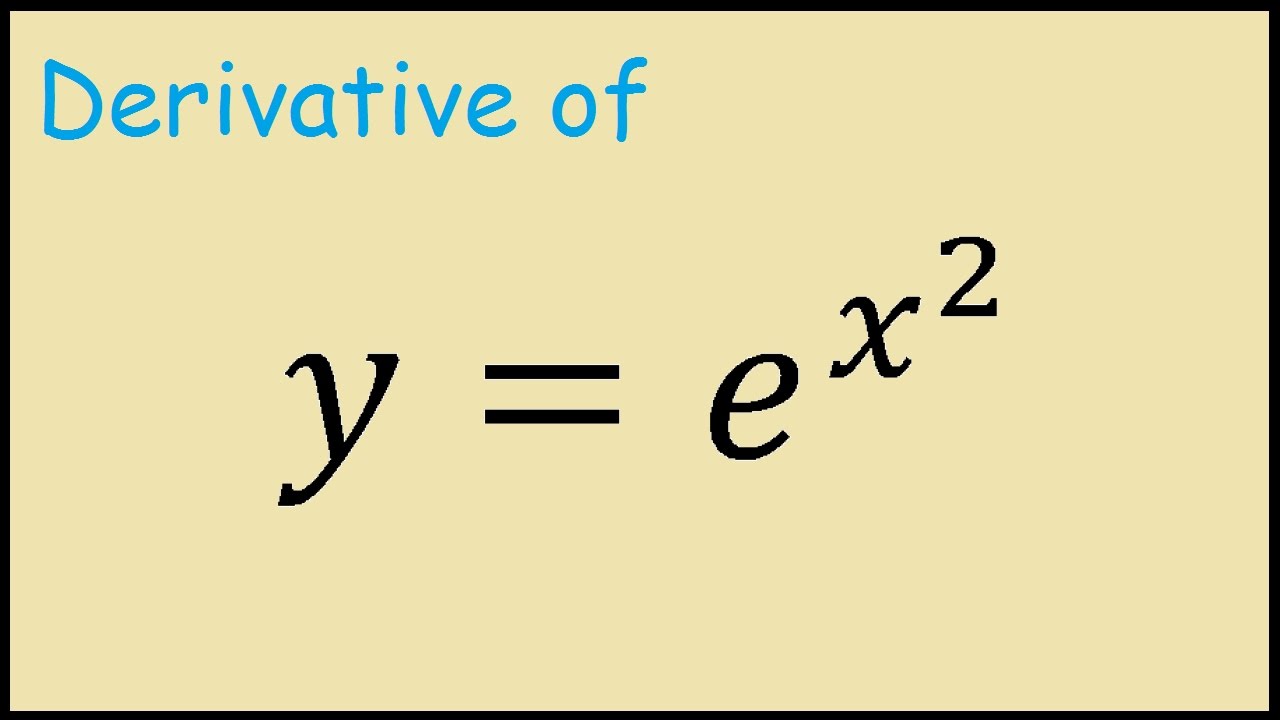



Derivative Of Y E X 2 Youtube
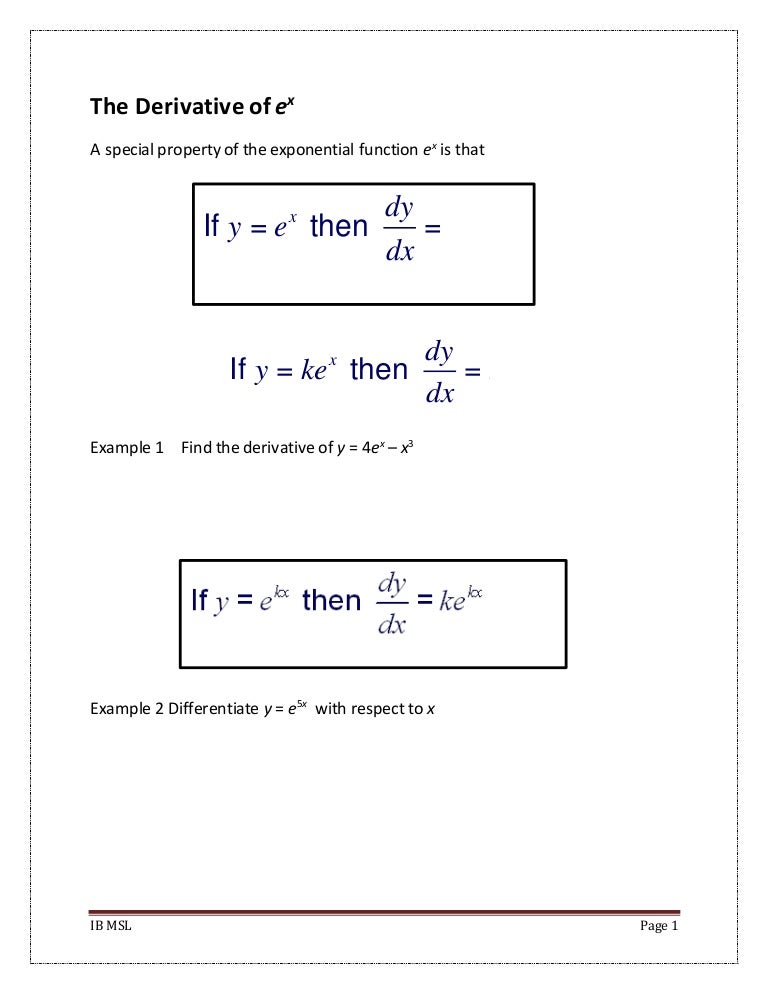



The Derivative Of E X And Lnx




How To Show That E E X Mid Y Mid Y E X Mid Y Mathematics Stack Exchange



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿